| |
|
| |
|
| |
| Definitions | For all who are interested in sailing we want start here with few common explanations about sailing and the used |
| | boats. |
| |
| | As you can read in Wikipedia. In opposite to the german definitions where you have a separation in so called Jollen |
| | and Yachts you will find here a bit different categories: |
| |
| | A sailboat or sailing boat is a boat propelled partly or entirely by sails. The generic term covers a variety of |
| | boats, larger than small vessels such as sailboards and smaller than sailing ships, but distinctions in the size |
| | are not strictly defined and what constitutes a sailing ship, sailboat, or a smaller vessel (such as a sailboard) |
| | varies by region and maritime culture. |
| |
| | Following the german basic separation Dhingies are able to capsizal, that means they can turn. That happens if |
| | the wind pressure is on one side of the boad bigger to the sail than on the other side the water pressure to the |
| | fin. The boats cannot sink because they have a lot of buoyancy, which avoid that they sink even they are full |
| | with water. All other boats with a bottom (in german they are called Kielboote) cannot capsizal because of a big |
| | weight in their fin or somewhere else under water. Beside there are so much different types of boats which are |
| | described very well in books or in the internet. |
| |
| | At least all sailing boats have a similar built-up: |
| |
| | • Hulk |
| | • Rigg |
| | • Canvas or Sail |
| |
| | With the small sketch from german Wiki we would like to show the what is what. Sorry that it is in german, I |
| | was not able to find another pic which explain it in english. |
| |
| | 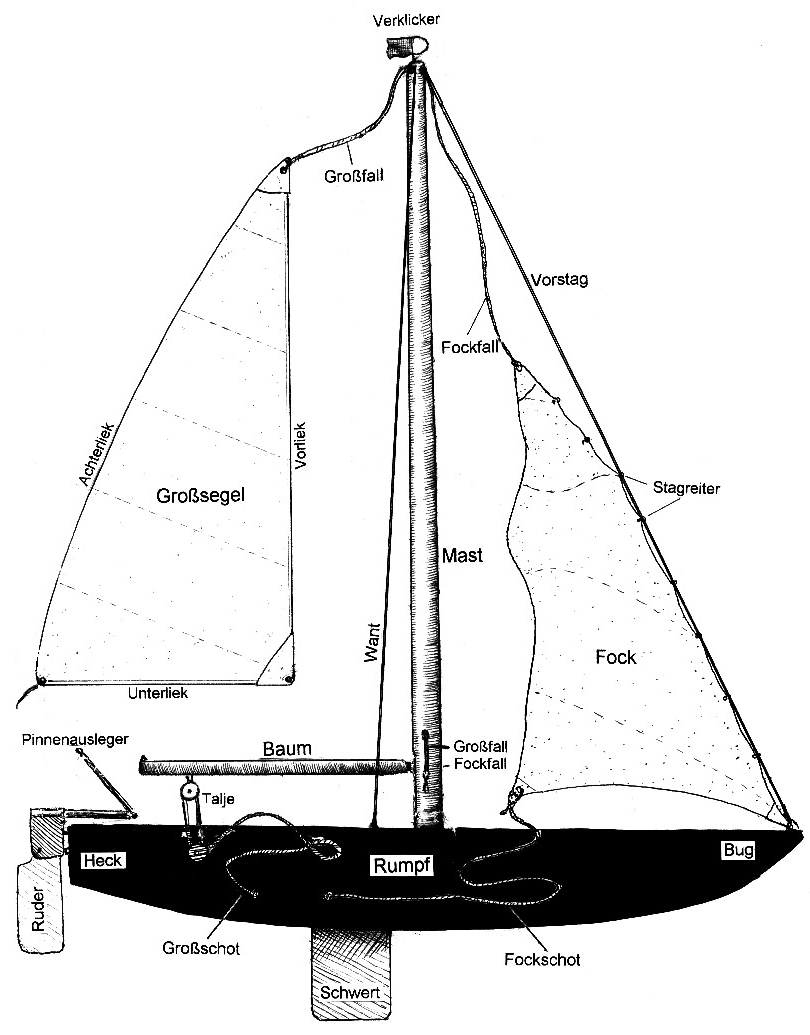 |
| |
| | The hulk |
| |
| | As written above we separate Boats mainly by the type and the form. Beginning with the used material for the |
| | hulk, which depends too if the boat will be used more for sport interests or just a family tour the boats |
| | will look different and will react different as well. Materials for boats are: |
| |
| | • Wood (today quite rare) |
| | • Ply wood |
| | • Steel |
| | • Aluminium |
| | • Plastics (specially the composite built) |
| |
| | If you built up a hulk in a classic way with wood, this will consists by a skeleton, where lengthwise connections |
| | will be built up with crosswise connections. The backbone will be built with the stem bar (german: Vordersteven) |
| | and the stern frame (german: Achtersteven). At the keel are the ribs connected. Further, to make the construction |
| | more stable you have some bracket plates (german: Bodenwrange). Lengthwise the stabilization will be done by the |
| | so called stringer. They are connected to the ribs (german: Spanten) as well. At the upper end of that ribs, |
| | they all will be connected with eachother with the so called Clamp (german: Balkweger), where the beam |
| | (german: Decksbalken) will be connected too. On smaller boats you will find the so called Mirror (german: Spiegel). |
| | [Source: OVERSCHMIDT/GLIEWE: Sportbootführerschein Binnen, Segel und Motor] |
| |
| | The hulk can show different forms like for example (sorry about the german kinds and types, I did not find how it |
| | is called in english): |
| |
| | • Rundspant |
| | • Knickspant |
| | • Katamarane |
| | • Trimarane |
| | • Spitz- or V-Boden and many more |
| |
| | All those forms have a different influence on the water and sailing. Here the lateral plan, so the part of the |
| | hulk which is under water, has a central signifiance. It works against the sideway drift. |
| |
| | Further you differ between different bow (front part, german: Bug) and stern (back part, german: Heck) forms |
| | (Sorry again for the german types): |
| |
| | • Yachtheck |
| | • Kanuheck |
| | • Plattgattheck |
| | • Gerader Steven (Steven ist der vordere Abschluß des Bugs) |
| | • Yachtsteven |
| | • Prahmsteven |
| |
| | The rigg |
| |
| | The rigg (german: Takelage) is the standing rigg and parts of the running rigg of a Sailing Boat. More in |
| | detail this are the (standing) masts and the hemp ropes, which fix the masts (shrouts, stays), and the spars, |
| | blocks and fittings, when they are connected to the masts and spars, and the part of the running rigg which |
| | is needed to handle the canvas, but not fixed somewhere on the ship. Not part of teh rigg are the canvases |
| | itself and the sheets, even they are part of the running rigg. (Translation from the Definitions of the german |
| | Wikipedia) |
| |
| | The sail |
| |
| | When you check in Wikipedia you will find the following definition of a Canvas/Sail: |
| |
| | A sail is any type of surface intended to move a vessel, vehicle or rotor by being placed in a wind—in |
| | essence a propulsion wing. Sails are used in sailing. Depending on for which boat type a sail was made you |
| | will find really much forms and different types. But a good separation, specially with small boats is the |
| | main sail and the fore sail. Depending on the size the fore sail can be a Fock or a Genoa (this sail reach |
| | over the mast and is used when the wind is lower). |
| |
| | 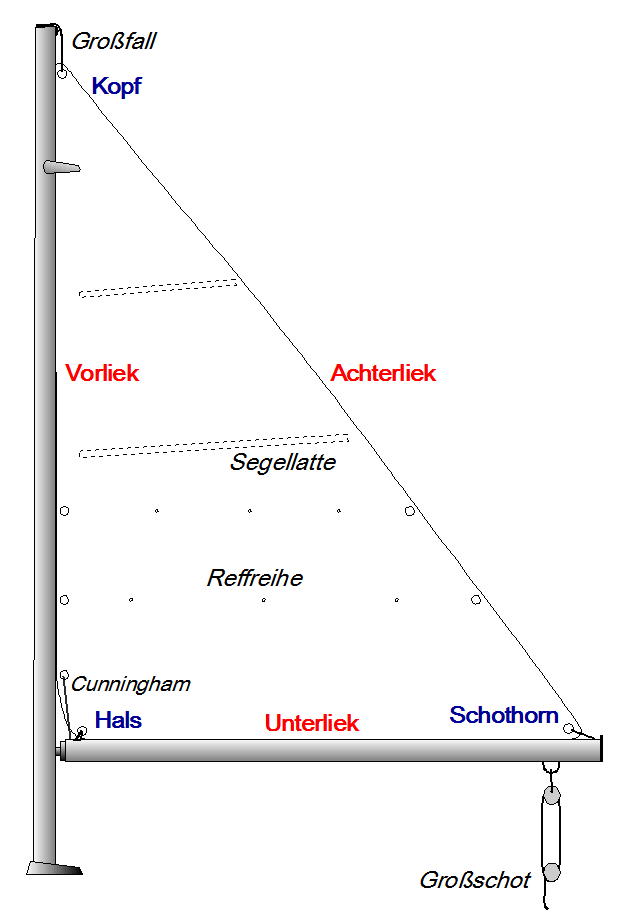 |
| |
|
| |
| Sailing licences | Overview of the sailing licenses of the German Sailing Association (DSV) |
| |
| Sailing licences | Bootsschulen AquaFun |
| | We have no experiances with this school, just it is the nearest |
| |
| Education pages and tools | NauticTools |
| |
| Nautic laws | International Rules to avoid collisions (German: Kollisionsverhütungsregeln, KVR) |
| | German Sea Traffic Law (Seeschifffahrtsstraßenordnung, SeeSchStrO) |
| |
|
| |
| Will follow soon |


